GL Anomaly Detection: General Information
The GL anomaly detection service can be used to avoid issues with GL transactions. The system will help you to recognize potential mistakes in posted transactions based on the system's analysis of abnormal amounts posted to a particular account, subaccount, branch, module, vendor, or customer. It will reduce the time for error resolution and improve the accuracy of these transactions.
Learning Objectives
In this chapter, you will learn how to do the following:
- Perform the training of the model based on reclassified transactions
- Analyze the transactions
Applicable Scenarios
You detect GL anomalies in the following cases:
- On a regular basis, to check the correctness of posted transactions and to analyze the account balances.
- When closing a financial period, to identify and investigate reporting issues.
Overview of GL Anomaly Detection
To start using the GL anomaly detection service, you should enable the GL Anomaly Detection feature on the Enable/Disable Features (CS100000) form.
The GL Anomaly Detection feature uses a machine learning algorithm to calculate predictions of errors in posted GL transactions. The algorithm uses a machine learning model—a file trained to recognize certain patterns. The model is operated by a cloud service and is based on different anomaly types.
The training is performed on the Analyze Accounting Transactions (GL510000) form and consists of the following types:
- Initial training: The first step after the feature activation. For initial training, the system uses transactions posted in the most recent 18 calendar months. The latest date in the 18th month defines the period corresponding to this date. For example, if the type of financial periods in the system is Month, the system will use transactions from 18 periods, if the type of financial periods is 2 Weeks, the system will use transactions from 36 periods. Based on these transactions, the model calculates patterns and trains them on the period most recently sent from MYOB Acumatica.
- Continuous training: The training that goes on continuously as new data is loaded. Each time, the model is trained more specifically to recognize errors. Each new financial period has to be sent to the model to train it.
After the initial training, you analyze transactions on the Analyze Accounting Transactions form. On the Review Anomaly Predictions (GL406000) form, you can check the correctness of posted transactions. The system detects and highlights possible errors and assigns an anomaly score to each transaction.
Each transaction has four scores calculated based on different anomaly types, such as the following:
- Account
- Branch, account, and subaccount
- Account and inventory ID
- Account and customer or account and vendor
These four types are unique key parameters of a transaction based on which the model creates a data subset during training. When performing prediction, the model compares transaction data with this subset to detect anomalies. Subsets can be the following:
- Subset 1: Account ID: 1, Branch: 2, Subaccount: 3
- Subset 2: Account ID: 1, Branch: 2, Subaccount: 4
- Subset 3: Account ID: 2, Branch: 2, Subaccount: 3
You can mark a transaction as false detection by selecting the transaction and clicking Mark as Valid on the form toolbar of the Review Anomaly Predictions form or agree with the system's prediction and correct a highlighted error by reclassifying the transaction. For details on transaction reclassification, see Reclassifying Transactions: General Information.
Setup of GL Anomaly Detection
To set up the GL anomaly detection functionality, the system administrator performs the following actions:
- On the Enable/Disable Features (CS100000) form, enables the GL Anomaly Detection feature.
- On the Companies (CS101500) form, for each company whose data should be used in GL anomaly detection, selects the Use for Anomaly Detection check box in the Summary area.
Workflow of the GL Anomaly Detection Process
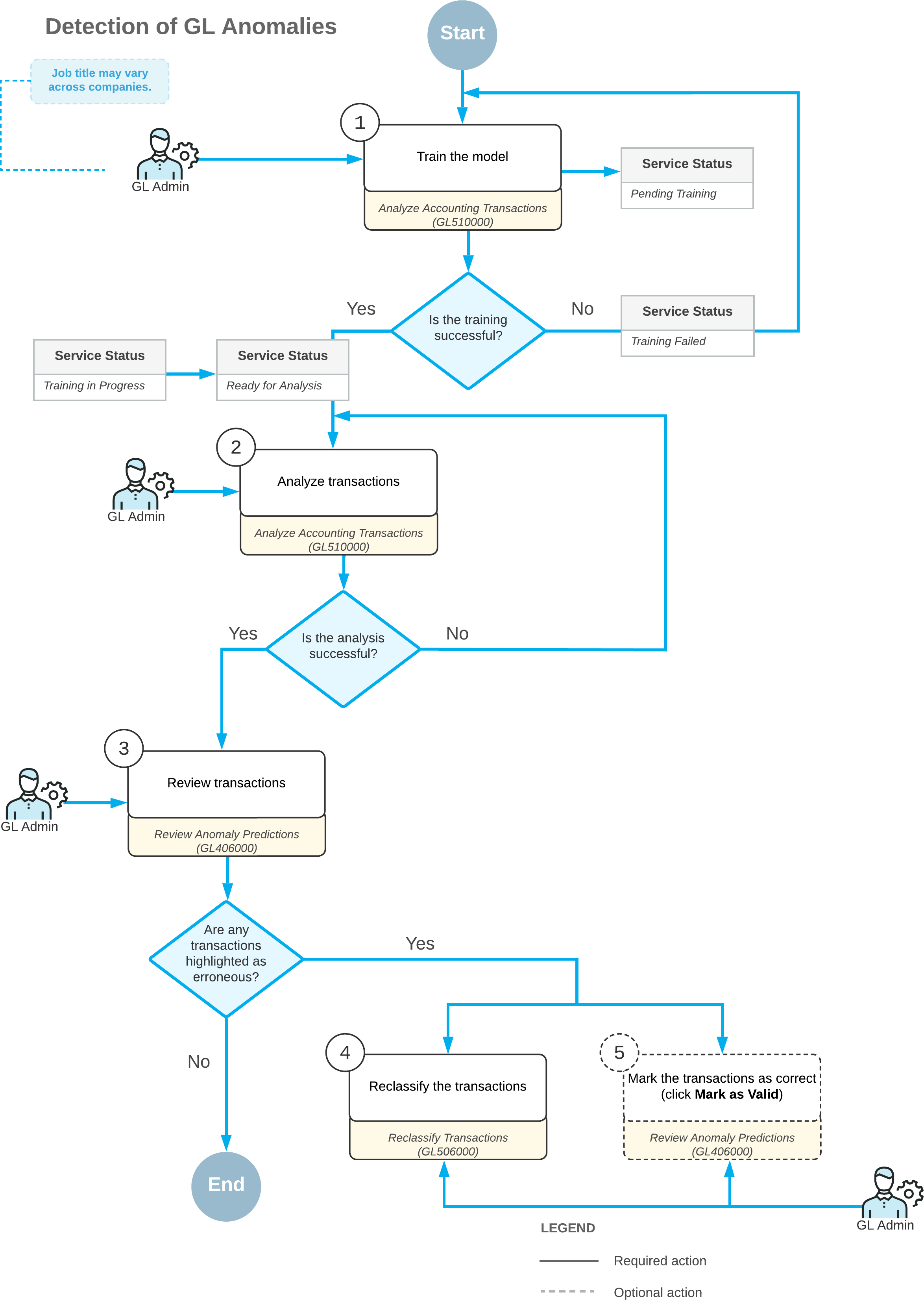
The workflow of GL anomaly detection is performed as shown in the diagram below.
The detection of GL anomalies includes the following steps:
- On the Analyze Accounting Transactions (GL510000) form, you train the model
based on the data from the selected company or companies. To train the model, you select
Train Model in the Action box and click
Process or Process All. Before the
training is started, the service status is Pending Training. If the training is
successful, the service status is changed to Ready for Analysis.
If the training is not successful, the service status is changed to Training Failed and you need to perform the training again.
- On the Analyze Accounting Transactions form, you analyze the transactions of the selected company or companies. To analyze transactions, you select Analyze Transactions in the Action box and click Process or Process All.
- When the analysis has been completed, you review the transactions on the
Review Anomaly Predictions
(GL406000)
form. On this form, you select the needed company or branch, the
financial
period,
and the needed account.
The
system loads the records to the table,
sorted first by
their status and then by their anomaly score in descending
order.
If any transactions have been highlighted as erroneous, you do either of the following:
- You select the transaction and click Reclassify on the form toolbar of the Review Anomaly Predictions form. On the Reclassify Transactions (GL506000) form, you reclassify the transaction (4 in the diagram below).
- You select the transaction and click Mark as Valid on the form toolbar of the Review Anomaly Predictions form (5 in the diagram below). (You can return the Pending Review status for this transaction if you select it and click Mark for Review on the form toolbar.)