Multitenancy Support (CompanyID, CompanyMask)
Multiple tenants can work on the same instance of an MYOB Acumatica Framework-based application with completely isolated data. The application looks identical to all tenants, but each tenant has exclusive access to its data only. Data is isolated at the lowest level of the application, in the data access layer that executes SQL queries for the tenant of the user who is currently signed in.
Multitenancy Support
The following graphic illustrates how different logical tenants work with the MYOB Acumatica Framework-based application in a multitenant configuration. They work with the same application but have isolated data access, as if they are working with different database instances.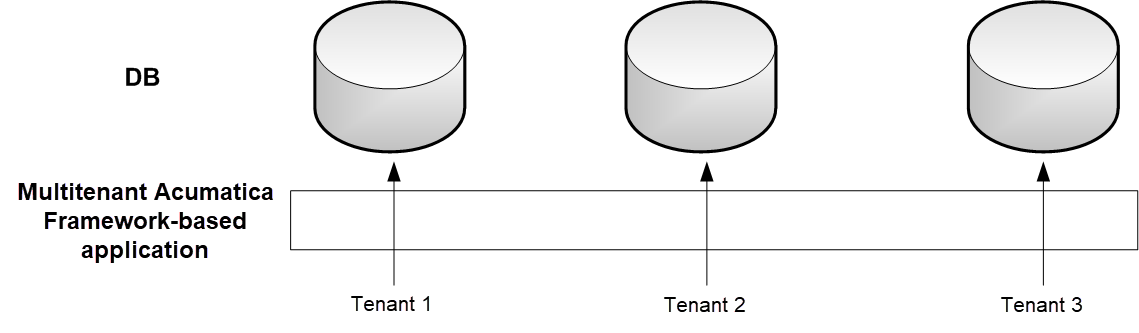
Multitenancy support is turned on or off for each particular table individually. To turn
on multitenancy support for a table, add the CompanyID column to it and include
the column in the primary key (see the column parameters in the table below) and all indexes.
The CompanyID column is handled automatically by the framework and should not
be declared in data access classes. If a table does not have the CompanyID
column, all data from the table is fully accessible to all tenants that exist in the database.
For more information, see Managing Tenants Locally and
Managing Tenants by Using the Web Interface.
| Database Column Name | Data Type (SQL Server) | Data Type (MySQL) | Type Attribute on the Data Field |
|---|---|---|---|
CompanyID |
int; not null; included in primary key and all indexes |
INT; not null; included in primary key and all indexes |
Not declared in DAC |
Support for Shared Data Access Between Tenants
MYOB Acumatica Framework
provides shared data access in a multitenant configuration. MYOB Acumatica Framework
supports a hierarchy of logical tenants that may work with a combination of shared and
individual data. In shared access mode, every tenant may work with its individual copy of a data
record; copies differ by CompanyID. All copies represent the same logical
object in the application but different data records in the database. For instance, each tenant
may use the individual settings of the application.
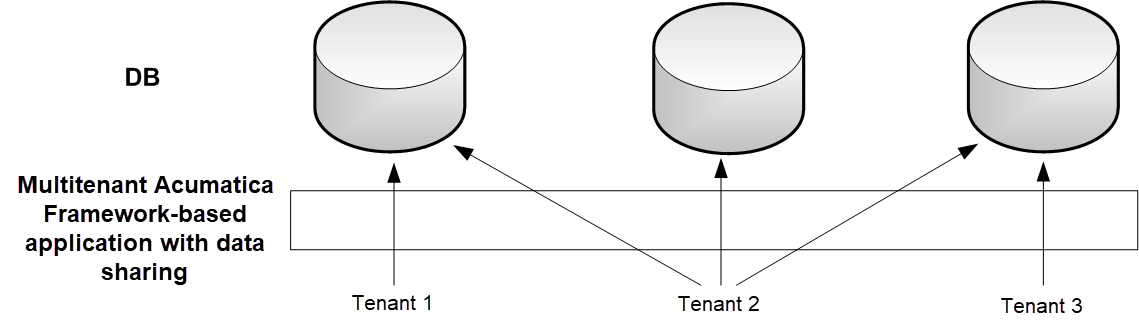
The graphic below shows a possible multitenant configuration with shared data access between Tenant 1, Tenant 2, and Tenant 3. The users of Tenant 2 have access to the data of all three tenants. The users from each of the other two tenants have access to their company's individual data only. Physically, the data of all three tenants is stored in a single database instance.
Support for shared data access is turned on or off for each particular table individually. To
turn on support for shared data access for a table, add the CompanyMask column
to the table (see the column parameters in the table below). The CompanyMask
column is handled automatically by the framework and should not be declared in data access
classes. If a table does not have the CompanyMask column, shared data access is
not available for this table.
| Database Column Name | Data Type (SQL Server) | Data Type (MySQL) | Type Attribute on the Data Field |
|---|---|---|---|
CompanyMask |
varbinary(32), not null, default 0xAA |
VARBINARY(32), not null, default 0xAA |
Not declared in DAC |
CompanyMask is a 32-bit mask. In this mask, each two bits correspond to each
tenant. The first of these two bits specifies whether the record may be read by this tenant, and
the second bit specifies whether the record may be written to by this tenant. For example,
suppose that CompanyMask is set to 0xBE02 for a record. That is, it specifies
the following mask: 10 11 11 10 00 00 00 10,
which designates that the record may be both read and written to by the tenants with company IDs
2 and 3, the record may be read by the tenants with IDs 4 and 5 and the System tenant (which has
ID 1), and the record may not be read or written to by other tenants.
CompanyMask: 10 11 11 10 00 00 00 10
CompanyID: 4 3 2 1 8 7 6 5The default value of CompanyMask is 0xAA, which means that the record may be
read by all tenants.
