Saving of Changes to the Database
A graph provides transactional saving of changes from all cache objects to the database. The graph commits the data to the database when you invoke the Actions.PressSave() method of the graph or when the user clicks Save in the UI. In both cases, the Persist() method of the graph is invoked. The Actions.PressSave() method also verifies that the Save action exists in the graph and is enabled. The Save action then invokes the Persist() method.
The graph commits changes from all cache objects within a single database transaction. If any row modification fails, the entire transaction is rolled back, and no changes from any cache object are persisted.
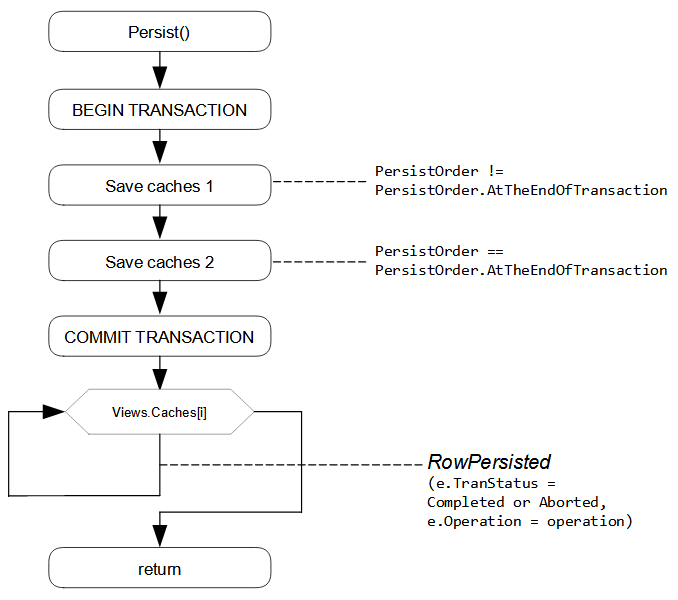
In the Persist() method, the system starts the database transaction (see the diagrams below). Within the transaction, the collection of cache objects is divided into two groups:
- DACs that are not marked with the
PXDBInterceptorAttributeattribute or its descendant, or have attributes with thePersistOrderproperty not equal to PersistOrder.AtTheEndOfTransaction - DACs whose attributes have the
PersistOrderproperty equal to PersistOrder.AtTheEndOfTransaction (for example, DACs that are marked with thePXAccumulatorAttributeattribute).
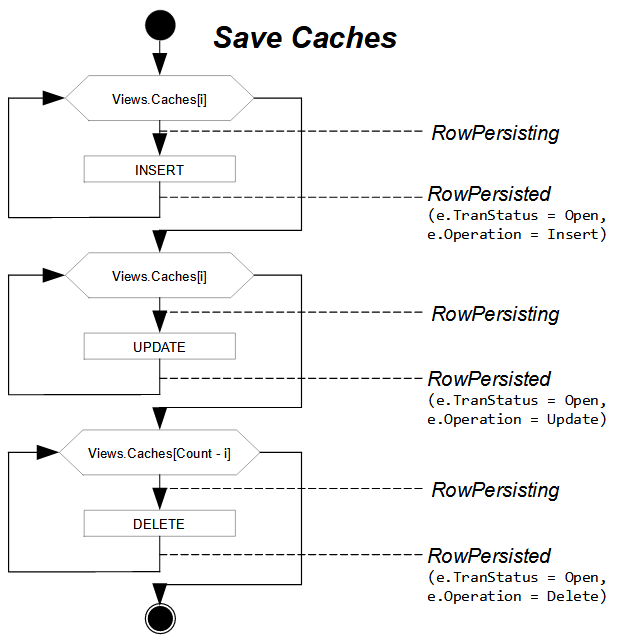
For each group, the graph iterates the collection of cache objects three times: for inserted records, for updated records, and for deleted records. First, all new records from all cache objects are inserted, and then all modified records are updated. Finally, within the same transaction, all deleted records are removed from the database. The graph iterates the collection of caches so that all master records are saved and then all detail records are saved.
In each iteration, the framework raises the RowPersisting event for a data record, executes the appropriate SQL command for this data record within the transaction, and then raises the RowPersisted event with the Open transaction status.
When the SQL commands have been executed successfully for all modified (inserted, updated, or deleted) data records, the graph commits the transaction. Regardless of the result of the transaction, the graph raises the RowPersisted event, in which you can check the status of the transaction. A successful transaction has the Completed status. If an error or exception has occurred during the transaction, the transaction returns the Aborted status. If the transaction fails, the modified data remains in cache objects. On the RowPersisted event for an aborted transaction, you can revert changed records to the default values.
When the RowPersisting event is raised, you can cancel the saving of a
particular row to the database by setting the e.Cancel property to
true in the graph handler for the event. For the sequence of events
raised for each modified row within the Persist() method of the graph,
see Sequence of Events: Saving of Changes to the Database.
