Sequence of Events: Saving of Changes to the Database
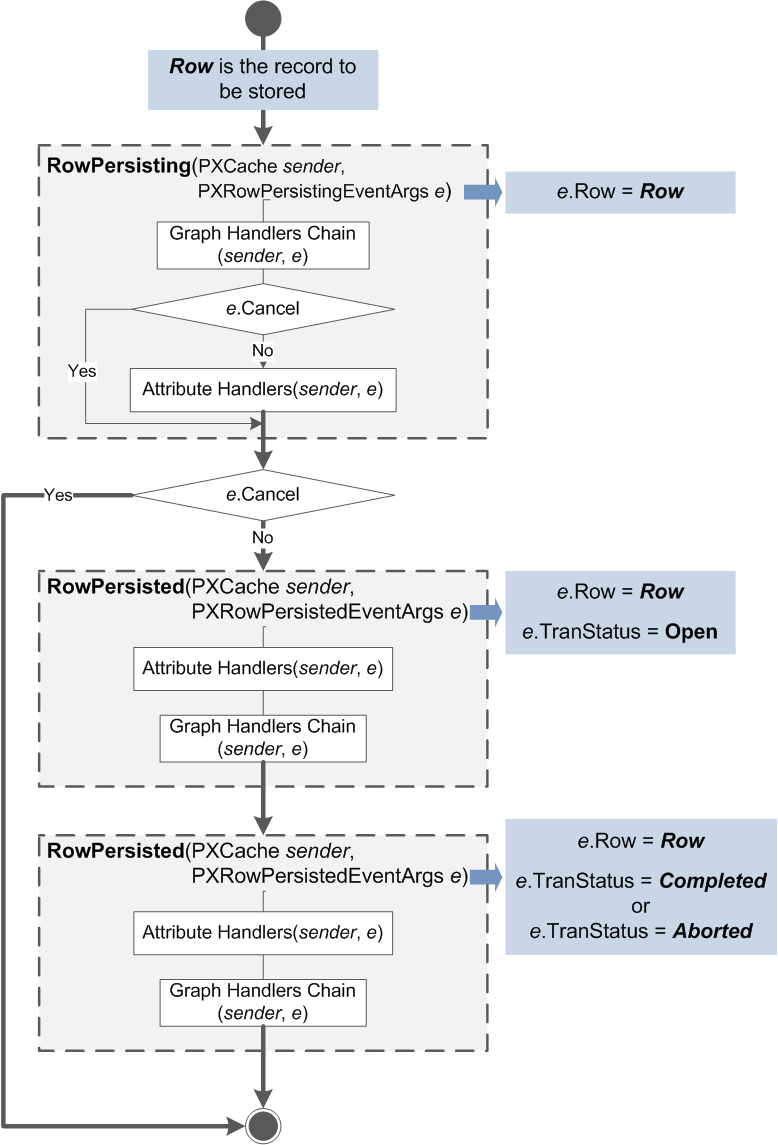
The following figure illustrates the sequence of events that are raised when a data record is saved.
While a user is inserting, updating, or deleting a data record, no changes are committed to
the database. The system stores the modified data records in the session, and you can access
them through the appropriate PXCache object. The system commits the
changes to the database when the user clicks Save in the user
interface, the save request is sent through the Web Service API, or
Actions.PressSave() is invoked on the business logic controller (BLC)
instance. In both cases, the Persist() method of the graph is
invoked. The Actions.PressSave() method additionally checks that the
Save action exists in the graph and is enabled. The
Save action then invokes the Persist() method.
When changes are saved to the database, events are raised as follows:
RowPersistingis raised. At this moment, a database transaction has already been opened. If any of the handlers setse.Cancelto true, the process will be canceled for the currently processed data record without an error being reported to the user. To cancel the process of committing changes and indicate the error to the user, you should throw the PXException exception.- If
e.Canceldoes not equal true:RowPersistedis raised. The commit operation for the current data record (available throughe.Rowin the handler) is completed, but the transaction is still open:e.TranStatusequalsOpen.RowPersistedis raised one more time, either withe.TranStatusequal to Completed (if all changes have been saved successfully) or withe.TranStatusequal to Aborted if an error has occurred and all changes have been canceled.
