CacheAttached: General Information
To replace attributes within a particular graph, you add new attributes to the
CacheAttached event handler for the particular field defined in the graph.
Learning Objectives
In this chapter, you will learn how to append and replace attributes on a specific data access class (DAC) field within a particular graph.
Applicable Scenarios
You replace attributes within a particular graph if in this graph, you need attributes that differ from the attributes declared in the DAC.
Attribute Replacement in a Graph
Attributes specified in a data access
class apply to this class in every graph of the application unless a graph replaces them with
other attributes. In some graphs, you may need attributes that differ from what is declared in
the DAC. To replace attributes within a particular graph, you add new attributes to the
CacheAttached event handler for the particular field defined in the graph, as
the following code shows.
// The CustomerMaint graph
[PXDBString(40, IsUnicode = true)]
// The field label for the form that works with the CustomerMaint graph
// is set to "Company".
[PXUIField(DisplayName = "Company")]
protected virtual void _(Events.CacheAttached<Account.companyName> e)
{ // Empty method
}Use of CacheAttached
The attributes that you add to a data field in the DAC are initialized once, during the
startup of the domain. You can replace attributes for a particular field by defining the
CacheAttached event handler for this field in a graph. These attributes are
also initialized once, on the first initialization of the graph where you define this method.
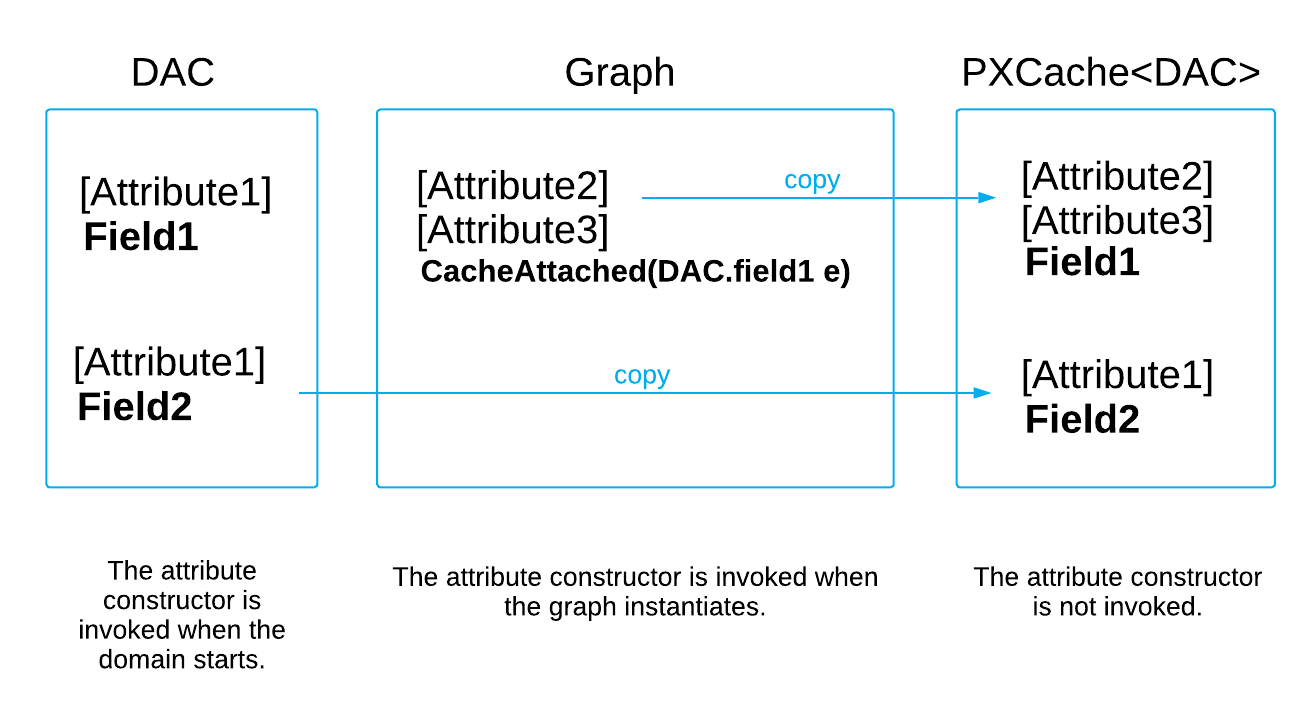
The system stores the attributes from the DAC and graphs (which are called domain-level attributes). On each round trip, the system copies the appropriate domain-level attributes to the cache object, creating cache-level attributes. Attribute constructors are not invoked; instead, the system invokes the CacheAttached(PXCache) method for each copy of an attribute. If you modify an attribute's properties in code for a particular data record, the cache object creates a data-record copy of the attribute.
In a graph, each PXCache object stores attributes for the corresponding DAC (see the diagram below). When a PXCache object is created, the framework searches for attributes of CacheAttached event handlers in the graph by using the DAC field name. Attributes specified for these event handlers are copied to PXCache objects. If there is no CacheAttached event handler defined for a DAC field, the attributes are copied from the data access class. The attributes of CacheAttached event handlers are instantiated once, on the first initialization of the graph in which you define this event handler. In the data access class, the attributes are instantiated when the application domain starts.
When you add an attribute to a DAC field, the attribute subscribes to particular events of the MYOB Acumatica Framework. In the corresponding event handlers, the attribute processes the field value based on the purpose of the attribute. For instance, the PXDefault attribute subscribes to the FieldDefaulting event and sets the default value every time the event is raised for the field. Multiple attributes can subscribe to the same event.