Consolidation Company Mapping Maintenance
You can access this form by clicking the Set up button on the Consolidation Code Maintenance form. The consolidation code and description are displayed in read-only format from the Consolidation Code Maintenance form from which this form was launched.
Options Reference
Each option and field on the form is described below. Mandatory options and fields are highlighted in red.
Subsidiary company
Select the subsidiary company for the mapping.
Consolidation company
Select the consolidation company to which the selected subsidiary company is mapped. You cannot set up a company to be a consolidation company in more than one consolidation code.
Main
Percentage ownership
This is set to 100, and is read-only.
Consolidation currency
This is set to the current company's currency code, and is read only.
Inactive
The default value is deselected to indicate the mapping is active. If the option is selected, the company mapping will not be displayed in the hierarchy diagram within Consolidation Code Maintenance, and will also not be available for selection when processing a consolidation using this consolidation code. You can still prepare the subsidiary company for consolidation.
Period mapping
If the subsidiary and consolidation companies are using different GL calendars, a period mapping must be selected to indicate how the financial periods are mapped between companies for the purposes of consolidation.
Use translated value
This is enabled if the Translations module is in use for both the subsidiary and the consolidation company. It indicates that the subsidiary's translated values must be used in the consolidation process. If the subsidiary company has a different base currency to the consolidation company, the option defaults to selected and read-only. If you select this option, the Transaction reserve account and Variance account fields are mandatory.
Transaction reserve account
This field is visible and mandatory if the option to Use translated value is selected.
It is used to specify the account that any foreign currency translation reserve amounts should be posted to. It is used by the Generate Consolidation process when generating journals for foreign subsidiary companies.
Variance account
This field is visible and mandatory if the option to Use translated value is selected (see above). It is used to specify the account that any foreign currency translation variances should be posted to. It is used by the Generate Consolidation process when generating journals for foreign subsidiary companies.
 Once specified,
all variances for foreign subsidiaries
will be posted to this account whether or not they are due to foreign
exchange differences, so this variance account should be monitored in
the same way that your normal suspense account is. For other subsidiary
companies (those that are not using translations), any variances will
still be posted as 'forced balance' values to the normal suspense account.
Once specified,
all variances for foreign subsidiaries
will be posted to this account whether or not they are due to foreign
exchange differences, so this variance account should be monitored in
the same way that your normal suspense account is. For other subsidiary
companies (those that are not using translations), any variances will
still be posted as 'forced balance' values to the normal suspense account.
Account Mapping
To consolidate multiple company ledgers, for each company mapping (subsidiary to consolidation) within a consolidation code, you must map each subsidiary's general ledger chart of accounts to the consolidation company's General Ledger chart of accounts before a successful consolidation process can occur.
A consolidation account mapping is a set of instructions (or rules) for mapping accounts from a subsidiary company to the consolidation company. When you subsequently transfer information from a subsidiary to its consolidation company, a general ledger consolidation journal is created in the consolidation company, using the subsidiary's mapping information.
Mapping
This form displays a table used to set up the account mapping rules.
Type
Accounts are mapped from the subsidiary company to the consolidation company. Accounts may be mapped based on:
- One to one: Mapping types Account, Account Pair, Account Range, Tree map accounts on a one to one basis.
- Many to one: Mapping types Range to Account and Tree to Account map accounts on a many to one basis.
 The process
does not support a one to many mapping, as the consolidation process always
takes 100% of the value of the subsidiary company into the consolidation
company.
The process
does not support a one to many mapping, as the consolidation process always
takes 100% of the value of the subsidiary company into the consolidation
company.
Mapping types available to select are:
Account
Each General Ledger account from the subsidiary company is mapped to an account in the consolidation company, on a one-to-one basis, in standard general ledger account sequence. This requires that the account codes of the two companies are identical.
Account Pair
Selected pairs of accounts between the two companies are mapped to each other. Select the subsidiary account in the Source From column and consolidation account in the Destination From column.
Account Range
A range of account pairs between the two companies are mapped to each other. Enter the range for the subsidiary company in the Source From and Source To columns, and the range it is mapped to in the consolidation company in the Destination From and Destination To columns.
Range to Account
A range of accounts of the subsidiary company are mapped to one account in the consolidation company. Enter the range for the subsidiary company in the Source From and Source To columns, and the account it is to mapped to in the consolidation company in the Destination From column.
Tree
This allows accounts within branches of a General Ledger account tree of the subsidiary company to be mapped to accounts within branches of a General Ledger account tree of the consolidation company.
Select the:
- Subsidiary company's tree in the Source From column.
- Branch in the Source To column.
- Tree it is to be mapped to in the consolidation company in the Destination From column.
- Branch in the Destination To column.
Press Shift+Enter to expand tree branches in the branch entry columns.
Tree to Account
This allows accounts within a branch of a General Ledger account tree of the subsidiary company to be mapped to one account of the consolidation company.
Select the:
- Subsidiary company's tree in the Source From column.
- Branch in the Source To column.
- Account is to mapped to in the consolidation company in the Destination From column.
Press Shift+Enter to expand tree branches in the branch entry columns.
Verify
Once the mappings have been saved, click this button to show the defined mappings, in the Verify Mapping tab, as seen in the examples below:
Example 1:
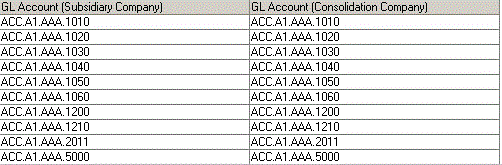
Account mapping has no errors
Example 2:
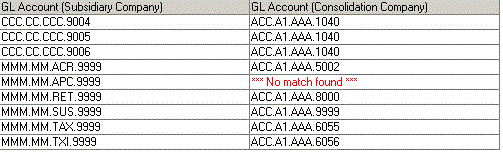
A subsidiary account is not mapped. The error *** No match found *** displays in the GL Account (Consolidation Company) column.
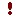 Any accounts
in the consolidation company that do not match any of the subsidiary company's
accounts are ignored.
Any accounts
in the consolidation company that do not match any of the subsidiary company's
accounts are ignored.
Example 3:
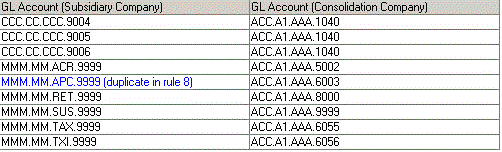
You can map a general ledger account to more than one consolidation account. This generates a Duplicate in rule warning. When consolidating, mapping rules are processed in table sequence so the first mapping found is used.
Example 4:
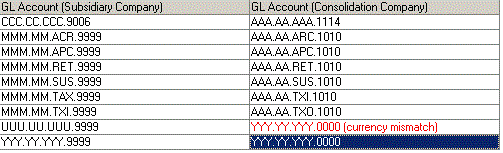
General ledger accounts must be mapped to an account of the same currency, unless the GF Translations module is in use, which enables a translation to be run before a consolidation, translating subsidiary values into the same currency as the consolidation company.
