Lists > Setting up tax codes
Tax codes are used to track tax paid to and by your business. Each tax code represents a particular type of tax.
Your software has an extensive list of tax codes that can be used in a variety of situations—for example, when doing business with overseas customers, when tracking capital acquisitions and so on.
When you create a tax code, you need to select which type of tax it is. There are eight tax types you can choose from. The table below describes what each tax type is for.
|
This tax type is used for taxes that are made up of two or more tax codes or sub-taxes.
|
|
|
Importers, who are bringing goods into Australia from other countries, should use this tax type. Tax codes with this tax type are used to record the import duty payable on a purchase order without changing the total amount of the purchase order. (The import duty is treated as a separate transaction since the duty is payable to the ATO, not to the company supplying the goods.)
|
|
|
Goods & Services Tax
|
This tax type is associated with the Goods & Services Tax assigned to sales and purchases. This tax type also is used for GST free goods and GST on Wine Equalisation Tax.
|
|
Input Taxed tax type
|
This tax type should be used by organisations, such as suppliers of financial services, that must pay GST on the purchases they make but don't collect GST from their clients or customers. The Input Taxed tax type also should be used by businesses that haven't registered for GST (businesses with turnover of less than $50,000 annually).
|
|
Luxury Car Tax
|
This tax type is used by the Automotive industry to handle the luxury car tax.
|
|
Voluntary withholdings
|
This tax type should be used for the PAYG voluntary withholdings scheme.
|
|
This tax type should be used for suppliers that have not quoted ABNs on their invoices, or for amounts that are withheld from investment income because no tax file number was quoted. This type indicates that the tax code is a PAYG Withholding tax type and will always be rounded down to the nearest dollar.
|
|
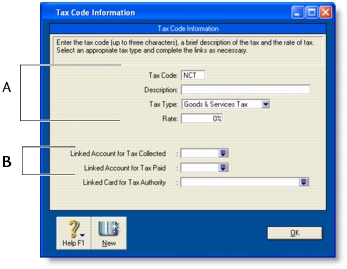
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
Enter a description, type and rate. If you selected Consolidated as the Tax Type, see ’Consolidated tax codes’ below.
|
|
|
Select the linked account for tax collected and for tax paid. These fields are only available for some tax types.
|
|
You can create consolidated tax codes by combining two or more tax codes. For example, you could create a GW tax code (with a 41.9% tax rate) that is composed of WET (Wine Equalisation Tax) at 29% and WEG (GST on Wine Equalisation Tax) at 12.9%.
note : You can only consolidate tax codes that are in your tax code list
Make sure you first create the tax codes you want to consolidate. The rest of the fields are filled in for you and the consolidated tax rate is calculated automatically.
You can assign a tax code to any detail account in your accounts list. The tax code you assign will appear as the default tax code in a transaction where you allocate a deposit, cheque, or a non-item sale or purchase to this account.
For example, you have assigned the GST tax code to your electricity expense account. When you write a cheque to settle your electricity bill in the Spend Money window, and allocate it to this account, the GST tax code will appear in this window by default.
You can allocate a tax code to an account in the Edit Accounts window. To open this window, go to the Accounts command centre, click Accounts List, double-click the required account, and click the Details tab.
You can assign a tax code to be used when you sell an item and a tax code to be used when you buy an item. That tax code will appear as the default in sales and purchases of that item unless you have specified that the customer’s or supplier’s tax code to be used instead.
Tax codes are assigned to items in the Buying and Selling tabs of the Item Information window. For more information, see Creating items.
You can define a default tax code for a customer or supplier. You would only need to select a default tax code if the customer’s or supplier’s tax status takes precedence over that of the item or service being sold or purchased.
For example, if a customer is one to whom you only ever make export sales, you should assign the EXP (Export Sales) tax code to that customer’s card.
When you create a quote, order or invoice, the tax code assigned to the customer will be used as the default. This tax code will override the item’s tax code in an item sale, and the allocation account’s tax code in a non-item sale.
Make sure you select the Use Customer’s Tax Code option. (If this is not selected, the customer’s tax code will not be used, even if one has been assigned.)
Similarly, when you create a quote, order or bill, the tax code assigned to the supplier will be used as the default. This tax code will override the item’s tax code in an item purchase and the allocation account’s tax code in a non-item purchase. Tax codes are assigned to suppliers in the Buying Details tab of their Card Information window.
Make sure you select the Use Supplier’s Tax Code option. (If this option is not selected, the supplier’s tax code will not be used, even if one has been assigned.)
Related Topics